What is a Exponential Moving Average?
A Exponential Moving Average
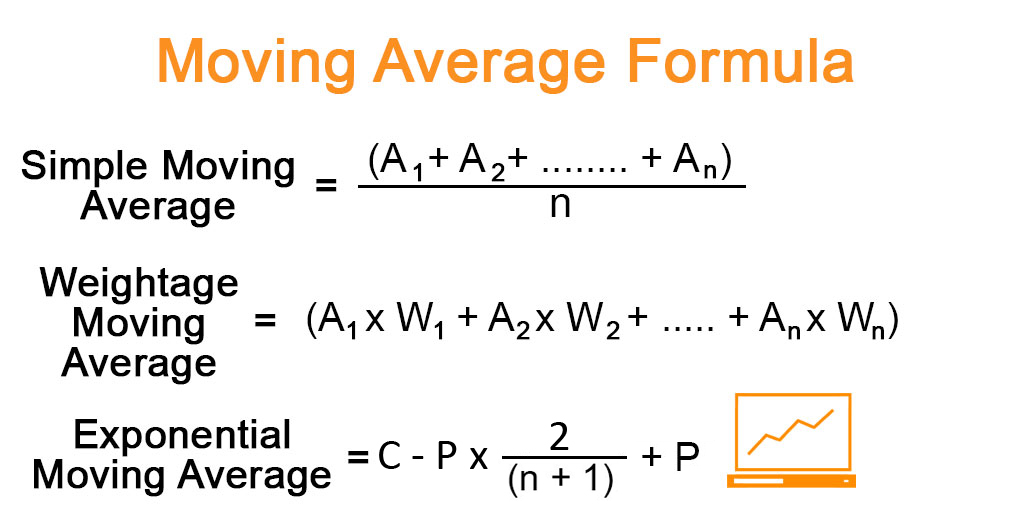 An Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a type of moving average that gives more weight to the most recent price data. Unlike a Simple Moving Average (SMA), which gives equal weight to each data point in the calculation, an EMA places a greater emphasis on recent price action.
The calculation of an EMA involves using a smoothing factor, which assigns a weight to each data point based on its position in the series. The most recent data points are given the highest weight, while older data points are given progressively less weight. The formula for calculating an EMA is:
EMA = (Price - EMA previous day) x (2 / n + 1) + EMA previous day
where:
Price = current price EMA previous day = the previous day`s EMA value n = the number of periods in the EMA calculation As the formula shows, the EMA calculation incorporates the previous day`s EMA value, which means that the EMA calculation is a recursive process. The smoothing factor, 2 / n + 1, determines the weight assigned to each data point, with a higher weight given to more recent data.
EMAs are often used by traders and investors to identify short-term trends and potential trading opportunities. A shorter-term EMA, such as a 20-day EMA, may be used to identify short-term trends, while a longer-term EMA, such as a 50-day or 200-day EMA, may be used to identify longer-term trends.
Like SMAs, EMAs can also be used in combination with other technical indicators to generate trading signals. For example, a bullish signal may be generated when the price of a security crosses above its EMA, while a bearish signal may be generated when the price crosses below its EMA. |
Latest Stock Market Tutorials
| 1. What is Descending Triangle Pattern? |
| 2. What is Bearish Pennant Pattern? |
| 3. What is Bearish Flag Pattern? |
| 4. What is Rising Wedge Pattern? |
| 5. What is Double Top Pattern? |
Free Stock Market Tutorials
| 1. Free Fundamental Analysis Course |
| 2. Free Technical Analysis Course |
| 3. Free Price Action Trading Course |
| 4. Free Futures & Options Course |
IMPORTANT ALERT! Information Posting in this website is only for educational purpose. We are not responsible for losses incurred in Trading based on this information.